Reliable Collection
for Remarkable Kitchens
Used cooking oil recycling
Our Services
USED COOKING OIL RECYCLING
With our hassle-free used cooking oil recycling service, we provide a convenient and responsible solution for disposing of your oil waste.
INEDIBLE MEAT BY-PRODUCT REMOVAL
Trust us to handle the timely pickup of your inedible meat by-products, allowing you to effectively manage your operations without any hassle.
FLEET SERVICES
With our comprehensive service and repair, Mopac is here to be your trusted local partner in maintaining and enhancing your fleet’s performance.
2023

Customer Rebates

UCO Recycled
GALLONS

Water Recylced
GALLONS
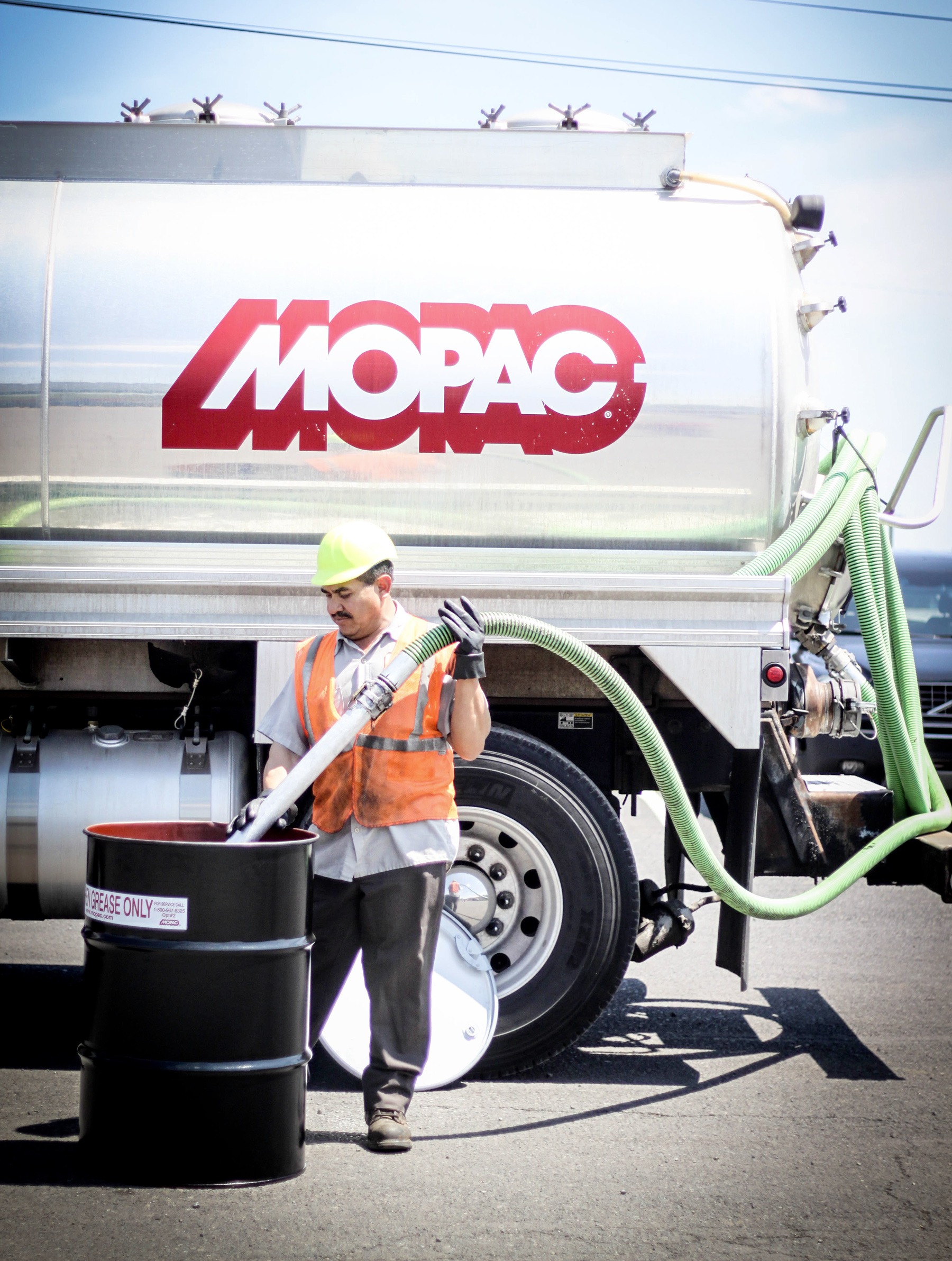

Reliable and efficient cooking oil recylcing
Your Oil, Our Mission
With over a century of experience in the recycling and rendering industry, MOPAC has been sustainably supporting the region since 1906. We specialize in the collection of used cooking oil and inedible meat by-products, transforming these waste materials into valuable resources. Our commitment is unwavering – we strive to achieve zero waste by recycling 100% of the materials we collect. Join us in making a positive impact on the environment. Contact us today and discover how our reliable collection service can provide a sustainable solution for your business.
Our Promise
At Mopac, we pride ourselves on our “set it and forget it” partnership with our customers. Our reliable and routine material removal services are designed with a focus on minimizing disruption to your daily business operations. Not only that, but we also prioritize the environment by recycling waste, reducing the overall environmental impact and carbon footprint. Trust Mopac for efficient and eco-friendly solutions.
We take pride in our mission to make a positive impact on the communities we cater to.
Discover the power of sustainability with Mopac. Our dedicated team is committed to revolutionizing the way used cooking oil is handled. By providing reliable collection services, we empower kitchens to make a positive impact on the environment. Together, let’s transform the way we recycle and repurpose cooking oil for a greener tomorrow.
Providing Value Everywhere We go
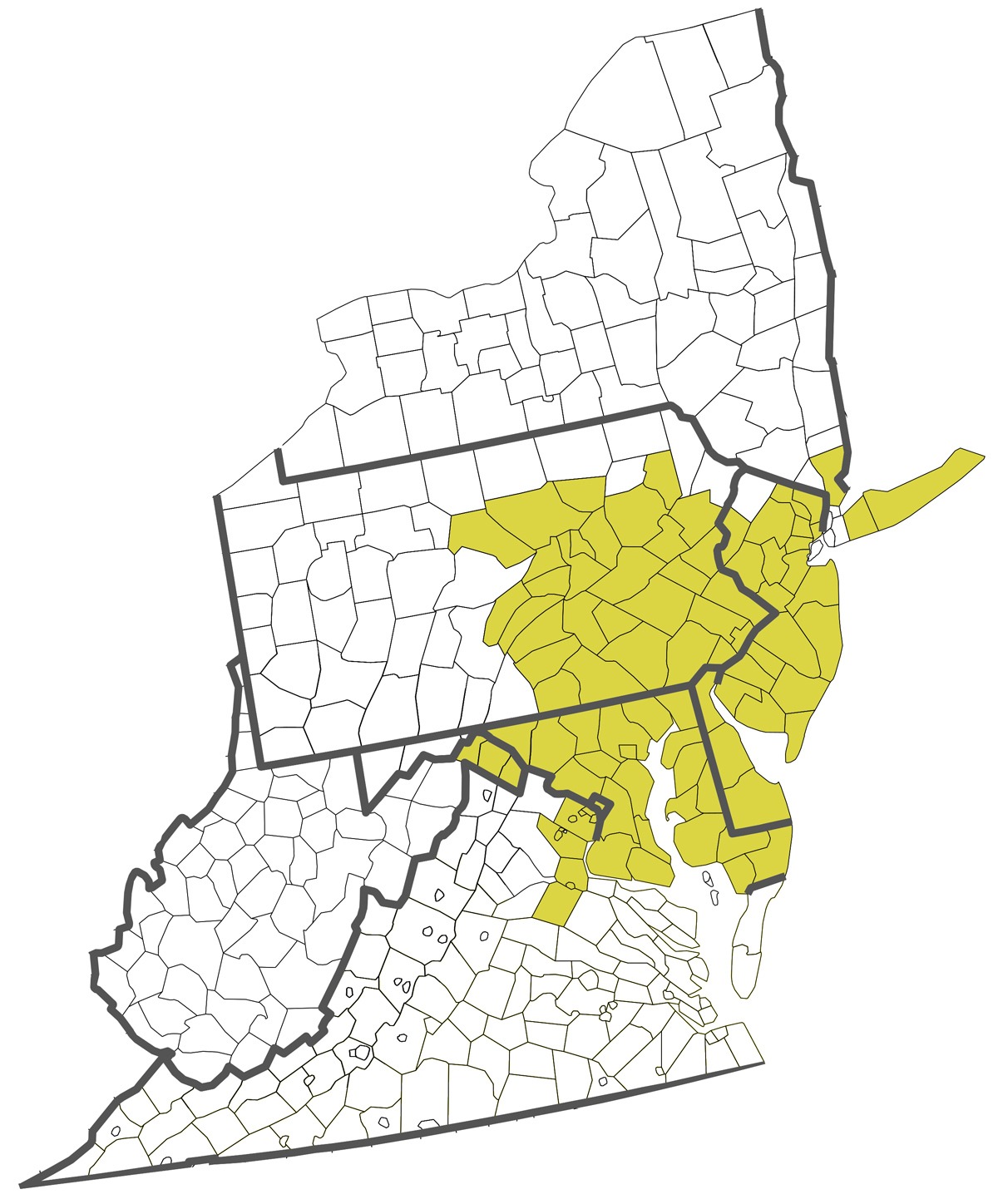
Service Areas
MOPAC specializes in catering to a diverse range of food service clients located in the Northeastern region of the United States. To learn more about our service areas, simply select a specific service below.